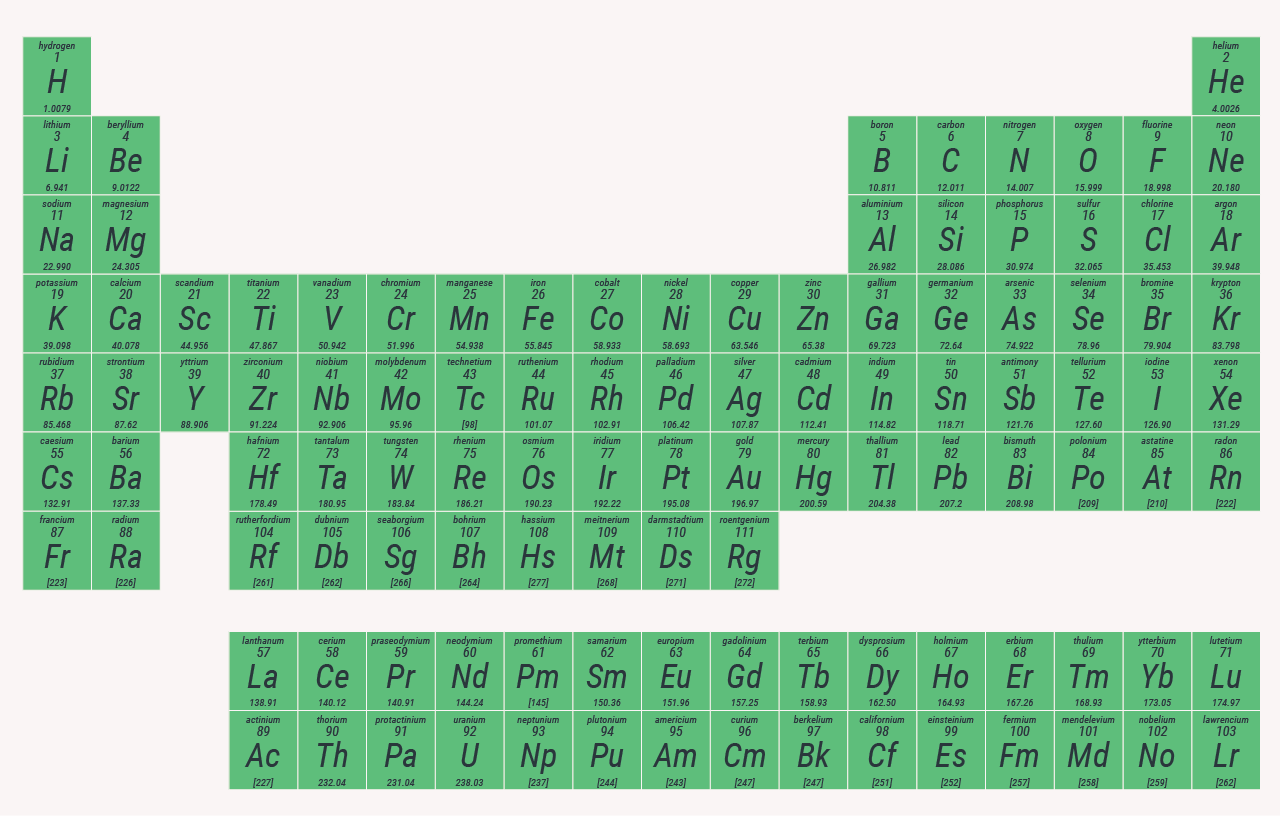

The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows and columns. It is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident.
The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as a dependence of chemical properties on atomic mass. As not all elements were then known, there were gaps in his periodic table, and Mendeleev successfully used the periodic law to predict some properties of some of the missing elements.
