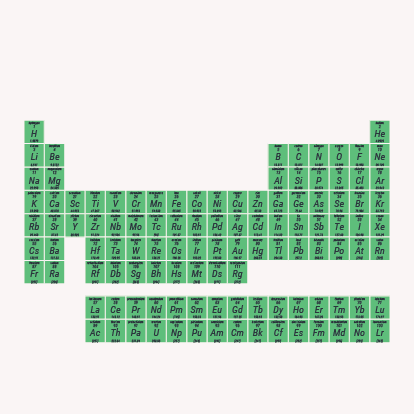
Atomic Number: the number of protons in their nucleus.
Mass number: the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the atomic nucleus.
Different isotopes of a given element are distinguished by their mass number, which is written as a superscript on the left hand side of the chemical symbol.
There is a total of 118 elements on the periodic table.
There are two versions of the periodic table, the 32-column or long form and the more common 18-column or medium-long form.